The Window Source The History of Energy Efficient Windows New Hampshire, Massachusetts, and Maine

Whether you are constructing a new house or renovating your existing one, you may be learning about the monetary and environmental advantages of energy efficient replacement windows. Did you know that the history of energy efficient windows is relatively brief?
Energy efficient windows are the product of about forty years of technological developments. It all began when the United States started searching for effective ways to reduce energy consumption. It was quickly apparent that windows were one of the largest contributing factors to heat loss in homes throughout the US. The Department of Energy estimated that 25% percent of all residential property heating costs were allocated to balance the impact of warmth loss over the windows.
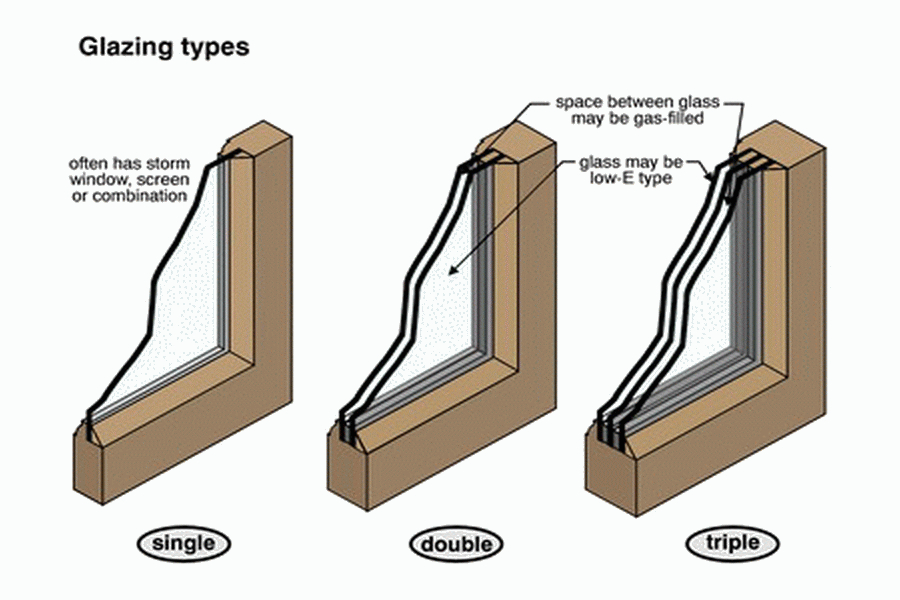
Most replacement windows sold in the US are single pane windows, which are often built with frames that are made of wood. During the late 1970s, multi-pane windows started to emerge in the market and “energy efficient windows” were introduced to Americans as a concept.
Multi-pane Windows
Having learned from the product of storm windows, the multi-pane windows made use of the gap between 2 or more sheets of glass as an “insulating layer”. While multi-pane windows were developed, the gap between the layers were filled with argon and other static gasses to enhance their protective properties.
Window Frames & Spacer Materials
Manufacturers quickly realized that frames made of aluminum were inefficient insulators and resulted in significant loss of heat. In the 1980s, manufacturers began producing wood-vinyl and vinyl compound frames. Such frames reduced heat transfer and it boosted the effectiveness of replacement windows. The spacers that held the window panes were also considered. Metal spacers were replaced with either plastic or foam spacers, both of which acted as better insulators and reduced both heat loss and condensation.
Low-E Glass
Low-e or low-emissivity glass was initially used in making energy efficient windows. The low-e glass makes use of a slim sheet of metal oxide that acts as a semi-permeable barrier to infrared radiation. Low-e glass permits visible light to pass through the glass, but helps prevent heat from entering or escaping your home.
Energy Efficient Windows of the Future
Researchers have begun developing new coatings which will permit the windows to alter depending on an electric current that responds to external conditions. AE or Absorbing Electrochromic windows make use of a slim sheet of material which changes the shade under a small electric current. A light sensor within the window can automatically change the amount of electrical current. These windows can be translucent during low-light states and darker when exposed to more sunlight.
Summary
The materials and construction of replacement windows are an important consideration for your home. We always advise calling a local professional (we serve all of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Maine) to come out and evaluate your home and provide you with personalized recommendations.
Window technology has changed quite a bit in the last forty years. At the end of the day, it is important to consider materials and budget. Call Window Source NH today for your free home evaluation.











